SpringMVC-常用注解
SpringMVC-常用注解
学习核心
基于Controller层的常用注解
| 注解 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 路径映射配置相关 | |
| @RequestMapping | 用于映射请求路径,可定义在类、方法上 如果定义在类上,则表示类中的所有方法都是以该地址作为父路径 |
| 请求相关 | |
| @RequestHeader | 获取指定的请求头数据 |
| @RequestParam | 用于指定请求参数名称 |
| @PathViriable | 用于从请求路径下获取请求参数(/user/{id}),传递给方法的形式参数 |
| @RequestBody | 用于接收http请求的json数据(将json转化为相应的java对象) |
| 响应相关 | |
| @Controller | 控制器配置(Bean注入配置) |
| @ResponseBody | 用于将controller方法返回对象转化为json对象,并响应给客户端 |
| @RestController | 其作用等价于@Controller + @ResponseBody |
案例分析
结合案例分析每个注解的应用场景(SpringMVC构建的基本案例参考SpringMVC核心,在此基础上填充案例进行注解测试)
1.@Controller
@Controller源码
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Component
public @interface Controller {
@AliasFor(
annotation = Component.class
)
String value() default "";
}
Controller定义
// 控制器定义
@Controller
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping(value = "index", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String hello() {
// 返回的逻辑视图名
return "index";
}
}
JSP定义(webapp/WEB-INF/views/index.jsp)
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh-CN">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<title>Index</title>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
hello SpringMVC
</div>
</body>
</html>
tomcat启动访问测试
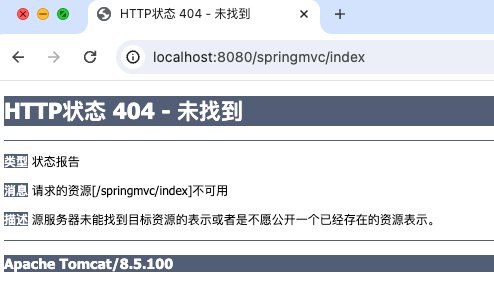
访问路径:http://localhost:8080/springmvc/index
访问结果:路由正常跳转,访问接口,最终定位到对应的index.jsp页面
对比@Compontent和@Controller,@Compontent是一个更为通用的注解,但是在Web应用程序开发中,基于MVC模式构建则需要严格按照分层规则进行Bean定义,否则无法正常被SpringMVC模块识别并构建。例如此处在HelloController中将@Controller调整为@Compontent重新发布部署再访问URL,就会发现提示404错误,是因为SpringMVC无法将一个@Compontent组件识别为一个控制器,因此在Web应用程序开发时要严格注意注解的使用
2.@RequestMapping
@RequestMapping源码
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Mapping
public @interface RequestMapping {
String name() default "";
@AliasFor("path")
String[] value() default {};
@AliasFor("value")
String[] path() default {};
RequestMethod[] method() default {};
String[] params() default {};
String[] headers() default {};
String[] consumes() default {};
String[] produces() default {};
}
@RequestMapping常用的三个参数
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| value | 指定映射的URL地址(例如案例中的index) |
| method | 指定映射的请求类型(如GET请求、POST请求等,参考org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod枚举) |
| produces | 指定返回的response的媒体类型和字符集(如application/json;charset=UTF-8,参考org.springframework.http.MediaType常量) |
结合案例说明
@RequestMapping注解的value属性还支持接受一个String类型的数组(用于限定不同的路径前缀,可通过其访问到相应的内容)
// 控制器定义
@Controller
@RequestMapping({"hello","myIndex"})
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping(value = "index", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String hello() {
// 返回的逻辑视图名
return "index";
}
}
访问:http://localhost:8080/springmvc/hello/index、http://localhost:8080/springmvc/myIndex/index
3.@ResponseBody
在上述的案例中,其实现的效果是通过访问到对应的控制器并执行方法,通过返回index(指向的是视图),这个方法执行会经由视图解析器最终定位到webapp/WEB-INF/views/index.jsp视图,随后直接返回一个页面给到前端。
但一些案例场景中并不需要返回一个页面,而是直接返回数据给前端,可以在方法中指定@ResponseBody注解(放在返回值或者方法上),用于将返回值放在response体内,而不是返回一个页面
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/anno")
public class DemoAnnoController {
@RequestMapping(value = "/index1", method = RequestMethod.GET, produces = MediaType.TEXT_PLAIN_VALUE)
@ResponseBody
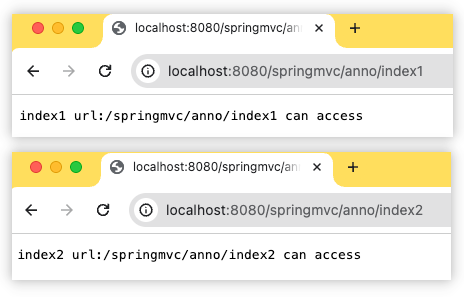
public String index1(HttpServletRequest request) {
return "index1 url:" + request.getRequestURI() + " can access";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/index2", method = RequestMethod.GET, produces = MediaType.TEXT_PLAIN_VALUE)
public @ResponseBody String index2(HttpServletRequest request) {
return "index2 url:" + request.getRequestURI() + " can access";
}
}
4.@RequestParam
@RequestParam注解用于接收URL中的参数信息。
在上述案例中添加方法进行测试
@RequestMapping(value = "/param", method = RequestMethod.GET, produces = MediaType.TEXT_PLAIN_VALUE)
@ResponseBody
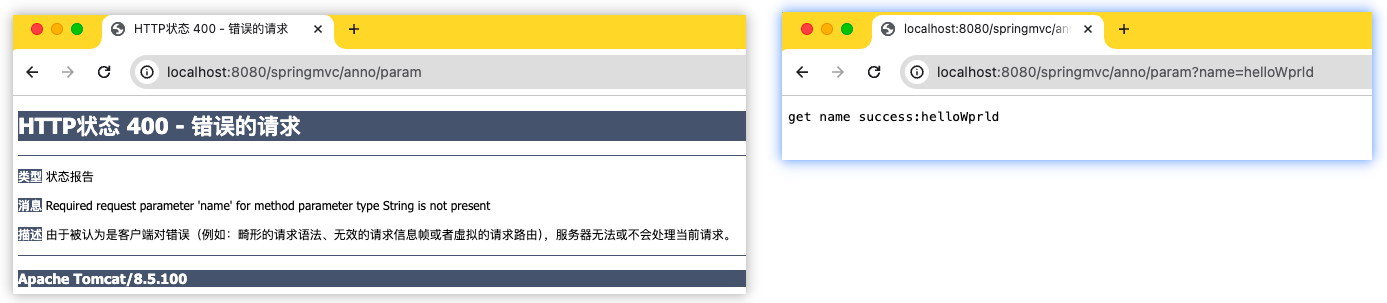
public String param(@RequestParam String name) {
return "get name success:" + name;
}
分别访问:
http://localhost:8080/springmvc/anno/param 访问失败提示参数错误
http://localhost:8080/springmvc/anno/param?name=helloWprld 访问成功正常获取参数
@RequestParam注解配置说明
上述案例中@RequestParam注解限定了该方法要接收一个名为name的参数,也可通过配置参数来灵活限定name的必要性
@RequestMapping(value = "/param", method = RequestMethod.GET, produces = MediaType.TEXT_PLAIN_VALUE)
@ResponseBody
public String param(@RequestParam(defaultValue = "001") String id,@RequestParam(required = false) String name) {
return "get name success: id :" + id + " name : " + name;
}
分别访问:
http://localhost:8080/springmvc/anno/param
http://localhost:8080/springmvc/anno/param?name=helloWorld
http://localhost:8080/springmvc/anno/param?id=008
http://localhost:8080/springmvc/anno/param?id=008&name=helloWorld
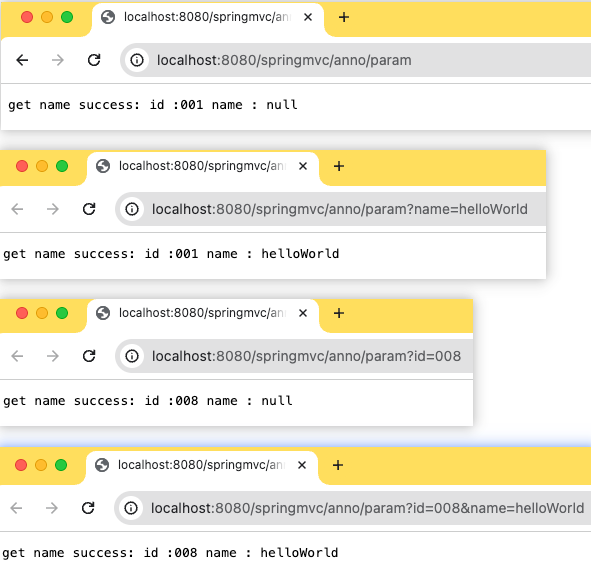
结合上述操作结果,可以看到,通过defaultValue属性可以给指定参数设定默认值,required属性可以限定该参数是否必传,在实际业务场景中可以择选
异常参数传递测试
基于上述案例,如果传入不匹配的参数类型则访问失败(URL中指定的参数类型和方法中定义的参数类型不匹配)
@RequestMapping(value = "/param", method = RequestMethod.GET, produces = MediaType.TEXT_PLAIN_VALUE)
@ResponseBody
public String param(@RequestParam(defaultValue = "001") int id,@RequestParam(required = false) String name) {
return "get name success: id :" + id + " name : " + name;
}
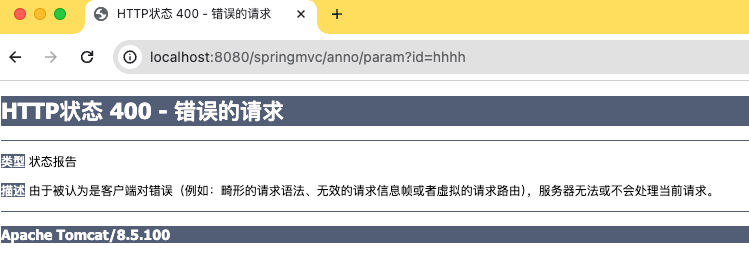
11-Jun-2024 09:33:10.221 警告 [http-nio-8080-exec-9] org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractHandlerExceptionResolver.logException Resolved [org.springframework.web.method.annotation.MethodArgumentTypeMismatchException: Failed to convert value of type 'java.lang.String' to required type 'int'; nested exception is java.lang.NumberFormatException: For input string: "hhhh"]
5.@PathVariable
@PathVariable注解也是用于接收URL中的参数信息,不过和@RequestParam注解稍有不同。
@PathVariable注解用于解析Url中的路径参数,例如https://www.cnblogs.com/xxxxxx/中的xxxxxx部分,而@RequestParam注解用于解析Url中的查询参数,如https://www.cnblogs.com/posts?page=2中的page部分
@RequestMapping(value = "/pathVar/{str}", produces = "text/plain;charset=UTF-8")
@ResponseBody
public String pathVar(@PathVariable String str) {
return "get name success: str :" + str ;
}
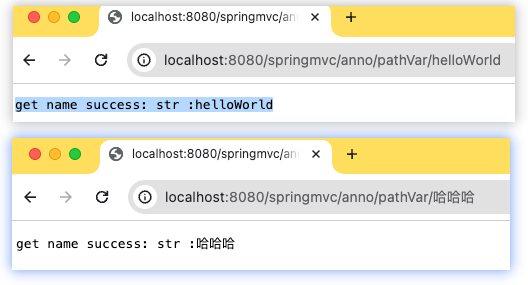
访问测试:
http://localhost:8080/springmvc/anno/pathVar/helloWorld
http://localhost:8080/springmvc/anno/pathVar/哈哈哈
此处方法参数和占位符名称相同,则可以省略value属性配置,但是如果@PathVariable中指定了value属性,它会假设占位符和方法参数名称相同(可以理解为一个绑定,将占位符和方法参数绑定)
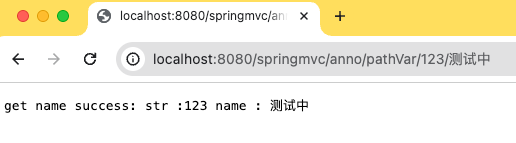
@RequestMapping(value = "/pathVar/{str}/{otherStr}", produces = "text/plain;charset=UTF-8")
@ResponseBody
public String pathVar(@PathVariable String str, @PathVariable(value = "otherStr") String name) {
return "get name success: str :" + str + " name : " + name;
}
6.@RequestBody
@RequestBody注解允许request的参数在request体中,而不是直接链接在地址后面,该注解放在参数前
7.@RestController
@RestController是一个组合注解,其作用等同于@Controller + @ResponseBody
案例分析
- pom.xml中添加依赖(用于对象和json转化)
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
<version>2.9.9</version>
</dependency>
- 新建DemoRestController进行测试
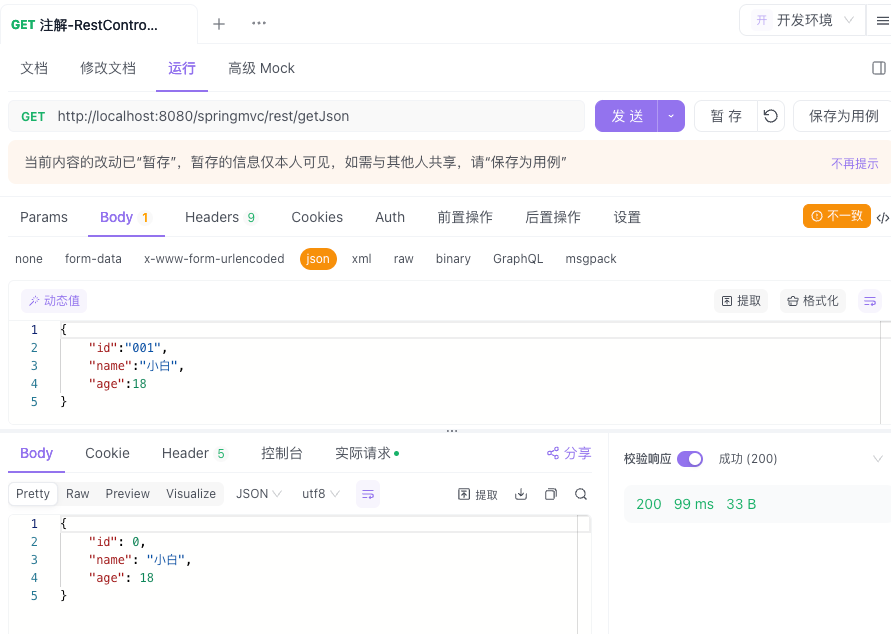
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/rest")
public class DemoRestController {
@RequestMapping(value = "/getJson", method = RequestMethod.GET, produces = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_UTF8_VALUE)
public User getJson(@RequestBody User user) {
return new User(user.getName(), user.getAge());
}
}
// 上述代码等价于@Controller + @ResponseBody 组合
@Controller
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/rest")
public class DemoRestController {
@RequestMapping(value = "/getJson", method = RequestMethod.GET, produces = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_UTF8_VALUE)
public User getJson(@RequestBody User user) {
return new User(user.getName(), user.getAge());
}
}
- 接口测试(使用ApiFox)